Types of Servo Motors
What is a Servo Motor
Servo motors are considered a part of a closed-loop system that includes a control system, amplifier, servo motor, and an encoder/resolver. A Servo motor is an electric motor that rotates parts of a machine with high efficiency and exceptional precision. A servo motor couples a regular motor with a sensor for positional interpretation that allows it to control the linear or rotational speed and position. In summary, a servo is a device that produces motion responding to a command and regulates the direction and speed of the motion produced in response to feedback.
Joseph Facort first used the term servo in 1859 when he controlled the rudders on a ship using steam. Servo motors are used in many products and devices that we use regularly. Servo motors are used in all computers and gaming consoles with a DVD player as the servo motor is responsible for the extension and retraction of the disk. Also, in all modern vehicles, a servo motor controls the throttle when the sensor detects the gas pedal is pushed. Most importantly, servos are widely used in aircraft, robotics, and industrial automation applications.
Types of Servo Motors
The main types of servo motors that we will discuss in our article are AC servo motors, DC servo motors, positional rotation servo motors, continuous rotation servo motors, and linear servo motors.
The first characteristic that defines an electric motor, and the servo motors, is the current they run in, which can be AC or DC.
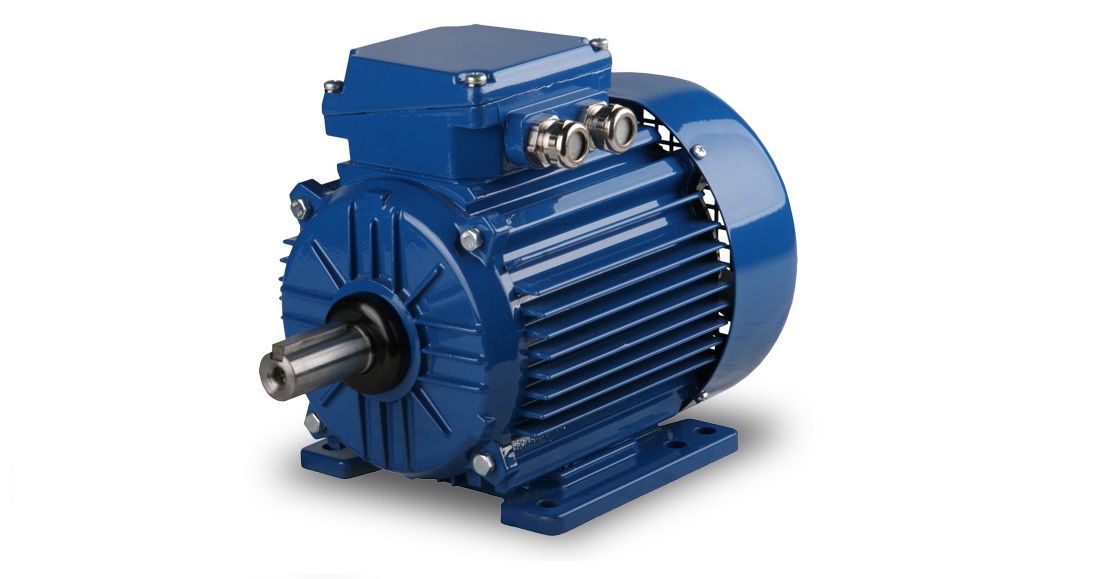
DC Servo Motor
As its name suggests, a DC Servo motor is a servo motor that runs on direct current, or in other words; it's a DC motor with sensors and encoders to provide feedback and closed-loop control. DC servos are not designed to take a lot of power surges and are better than ac servo motors for smaller applications. DC servomotors are commonly used in robotics, automation, and CNC machinery because of their versatility and high level of precision.
DC servo motors can be distinguished as brushed or brushless. Brushed DC motors are mechanically commutated with a commutator and brushed, while a brushless DC motor is electronically commutated with sensors. Brushless DC motors are more suitable for servo applications because they have higher efficiency and reliability than brushless motors, which are more prone to wear, especially at the brushes.

DC Servo Motor by Wittenstein
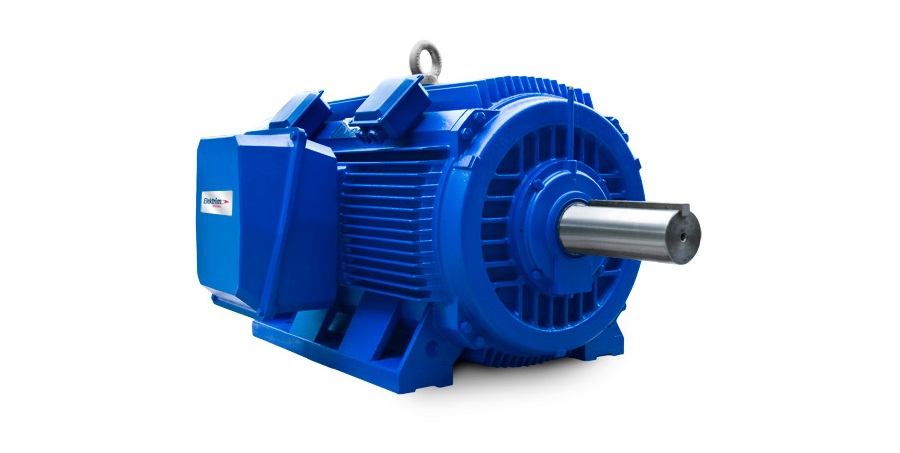
AC Servo Motor
An AC Servo Motor is a servo motor that runs on alternating current and consists of an encoder and a controller to control and receive feedback from the closed loop. AC servo motors are mainly used in high-precision applications. They can be designed to create even bigger torques by using higher voltages. They are more expensive, more efficient, and can handle more current surges than DC servos because of their superior design.
The two main types of AC motors are synchronous and asynchronous AC servo motors. They differ in the rotor's speed compared to the stator's. In a synchronous servo motor, the rotor's and stator's speeds are the same. While in an asynchronous servo motor, the rotor speed is less than the stator. Asynchronous servo motors, also known as induction servos, can yield more torque because of the slip caused by the speed difference between the shaft and magnetic field. There is no slip in synchronous servo motors because the stator and rotor are in sync and require an external AC power source. Synchronous servo motors are used in applications like power stations and manufacturing facilities, while asynchronous servo motors are used in centrifugal fans and compressors, conveyors, coffee machines, and lifts.

Synchronous Servo Motor by Stober
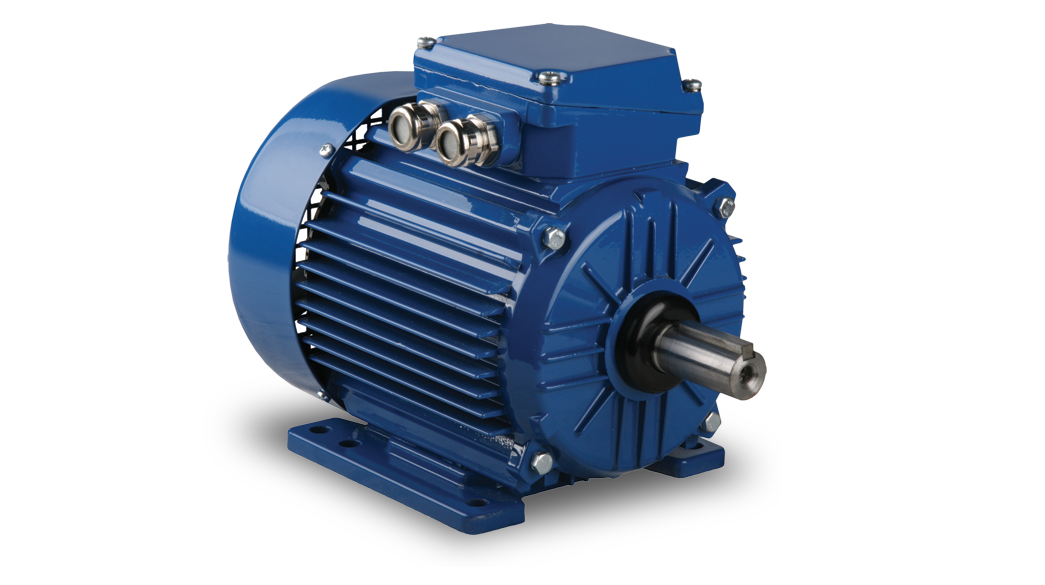
Also, three motion characteristics separate servo motors from each other: positional rotation servo motors, continuous rotation servo motors, and linear servo motors. The positional rotation servo motor is characterized by having the output of the shaft rotating at 180 degrees. Physical stops are placed in the gear to prevent outside rotation and protect the sensor. These positional rotation servo motors are mainly used in robotics, vehicles, and aircraft. Continuous rotation servo motors are similar to positional but can move in any direction. The controller of the continuous rotation servo motor is used to control the speed and direction of rotation(clockwise or anticlockwise) and is used in a radar dish.
In contrast, a linear servo motor is similar to a positional rotation servo motor. Still, it has an extra gear to change the output from circular to back-and-forth movement. Linear servo motors are used in new model airplanes as actuators.

Linear Servo Motor by Wittenstein
A servo motor is a particular motor class with low inertias and high response. It consists of a motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. They are designed for the most challenging environments, operating under extreme temperature conditions, for rapid-reversing and precision-positioning applications, such as inspection equipment, machine tools, packaging machines, and pick-and-place applications.
Feel free to Contact Us if you have any questions, need more information, or are interested in purchasing a servo motor.
Visit the following pages to learn about servo offerings: Servo Motors and Drives, Servo Gear Reducers, and Servo Geared Motors.
HVH Industrial is an authorized distributor of Wittenstein, Bonfiglioli, GAM, Apex Dynamics, NEUGART, Stober, and Heimotion. We work closely with their engineering teams to provide superior customer service and support.